
Unless the palpitations are caused by a heart condition, heart palpitations rarely require treatment. Instead, a health care provider might recommend taking steps to avoid the triggers that cause palpitations.
If palpitations are caused by a heart condition, such as an irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia), treatment will focus on correcting the condition.
Treatment depends on the cause of your palpitations. Your doctor will need to address any underlying medical conditions.
Sometimes, doctors aren’t able to find the cause. Heart palpations usually don’t require treatment unless your doctor finds they’re caused by an underlying condition.
If your palpitations don’t have a medical cause, you may be able to reduce symptoms by:
The most appropriate way to treat palpitations at home is to avoid the triggers that cause the symptoms.


Most commonly, the medication given is to suppress the heart beat or suppress the hearts electrical activity. Common drugs used are beta blockers (Bisoprolol, Sotalol, Metoprolol), calcium channel blockers (Verapamil, Diltiazem) or antiarrhythmics (Flecainide, Amiodarone) to slow down the heart rate and decrease the risk of complications.
One of the most common reasons people are referred to Cardiology Clinics, especially in younger people. The heart produces extra bursts of electricity in the top portion of the heart (the atrium) or bottom chambers of the heart (the ventricles). Ectopic beats cause the sensation of intermittent thumping, fluttering or missed beats. They occur most commonly when your resting – such as sat on the sofa or lying in bed at night before you fall asleep. These ectopics occur at other times, but the mind tends to ignore them if you are busy or pre-occupied. If an ectopic beat occurs, this can lead to anxiety which results in the body releasing adrenaline, irritating the heart, producing more ectopics – so a vicious cycle! Ectopic beats are further differentiated depending on the area of the heart affected.
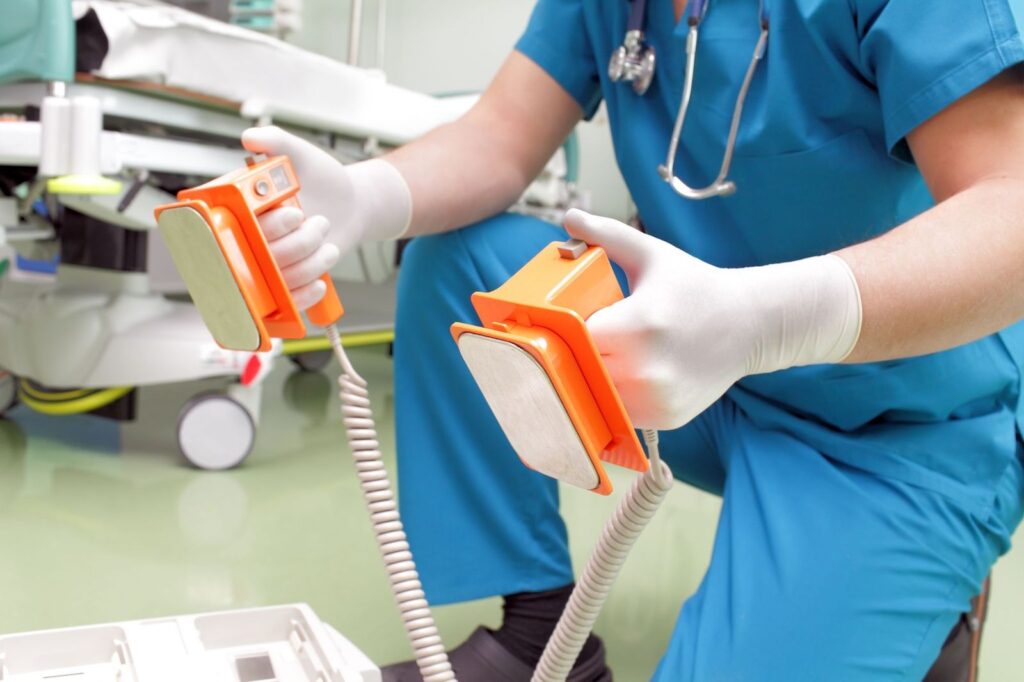
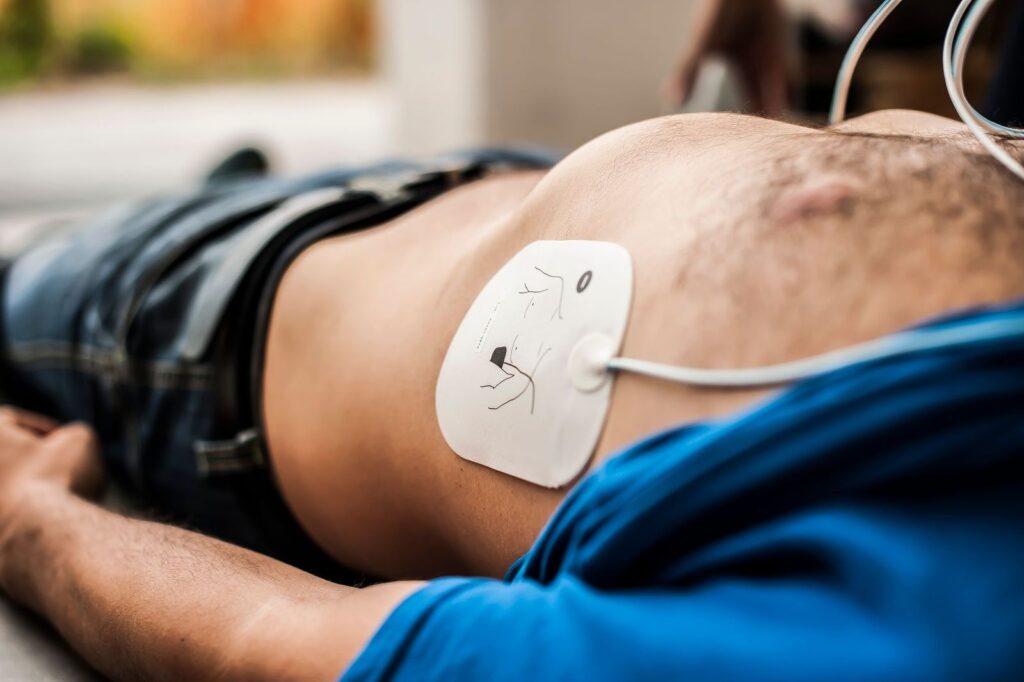



This is a minimally invasive procedure. A small plastic tube is placed in a vein in the groin or below
the collar bone and passed into the heart. It used to strategically destroy abnormal heart tissue
causing certain types of abnormal heart electrical activity such as Atrial Fibrillation, Atrial Flutter,
Occasional Ventricular Ectopics & Atrio-Ventricular Tachycardias. This procedure is normally
successful but can potentially be associated with risks & side effects. The risks are rare:
Pacemakers are devices implanted under the skin to correct a slow heartbeat. Implantable Cardiac Defibrillators (ICD’s) are devices that look like large pacemakers, implanted in a similar way but used to detect & correct life threatening electrical heart abnormalities by delivering a shock & restoring the hearts normal rhythm. Surgery: In rare cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or remove the source of any structurally abnormal tissue leading to problems in the hearts electrical activity.

Please call 0330 220 0332 or enter your details below & a brief summary of the problem & convenient days & times for you to speak to a Cardiologist privately.